1- What is the FNP?
-FNP phases
the passive stretch
is performed for 20 seconds, then the is performed for 8 seconds of isometric
contraction, it rests for 3-5 seconds and the passive stretches are performed
but amplified
Hamstring : is when you stand on the ground with your feet towards the wall and your partner pushes you slightly towards it to perform FNP phases
Cuadriceps: is when you stand against the wall and your partner grabs your leg by raising it up pushing you against the wall with the arm and performing FNP phases
2-General Syndrome of adaptión (G.A.S.) STAGES
< the “Father of Stress”, was a Hungarian endocrinologist and the first to give a scientific (1907 - 1982)explanation for biological “stress”. He actually borrowed the term “stress” from physics to describe an organism’s physiological response to perceived stressful events in the environment.
-
He eloquently explained his stress model, based on physiology and psychobiology, as the General Adaptation Syndrome (GAS), stating that an event that threatens an organism’s well being, a stressor, leads to a three-stage bodily response
-Stages of G.A.S.
1: Alarm
Upon perceiving a stressor, the body reacts with a “fight-or-flight” response and the sympathetic nervous system is stimulated as the body’s resources are mobilized to meet the threat or danger.2: Resistance
The body resists and compensates as the parasympathetic nervous system attempts to return many physiological functions to normal levels while body focuses resources against the stressor and remains on alert.3: Exhaustion
If the stressor or stressors continue beyond the body’s capacity, the resources become exhausted and the body is susceptible to disease and death.
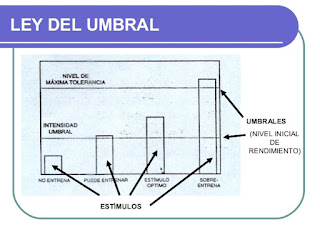
3-THRESHOLD LAW BY SCHULT
LAW OF THE THRESHOLD OR LAW OF ARNOLD-SCHULTZ. This is a part of the existence of a minimum threshold or estimate necessary for some modification, improvement or adaptation to occur in the body. ... In the first case it is very far from the threshold without training or improvements.
For example running with low intensity at the first times and them increased the intensity at the end and it can help to improve your resistance
4-WHAT IS THE TRAINING LOAD?
Training load is textual feedback on the strenuousness of a single training session. Training load calculation is based on the consumption of critical energy sources (carbohydrates and proteins) during exercise.
The Training Load feature makes the loads of different types of training sessions comparable with each other. For example, you can compare the load of a long low intensity cycling session to that of a short high intensity running session. To enable a more accurate comparison between sessions, we have converted your training load into an approximate recovery need estimation.
5-The principles of training acording to the classification of oliver (1985) and Zintl(1991)
Principles related to the stimulation of physical conditioning.
Principles related to the systems to which said stimulus is directed.
Principles related to the response to said stimulus.
-Zintl (1991) encompasses his proposed principles in three groups:
Those who initiate the adaptation.
Those that guarantee adaptation.
Those who exercise a specific control of adaptation.






No comments:
Post a Comment